Transport Layer Explanation – Layer 4 of the OSI Model
Did you ever wonder how the raw data (message) that the application from our desktop is transmitted over the Internet? By using the OSI model as a reference, we are able to understand how the raw data are transmitted from one host and received from another end-hosts without error. The OSI model has seven (7) layers. In this article, we will concentrate on Layer 4, which is the Transport Layer.
The upper layers, the Application Layer, Presentation Layer, and Session Layer, are responsible for preparing and sending the raw data. In contrast, the lower layers, the Network Layer, Data Link Layer, and Physical Layer, are responsible for encapsulating the raw data by using headers so that the network devices like routers and switches can understand and direct the traffic to the right device.
Contributions of the Transport Layer on Data Transmission
Transport Layer is responsible for end-to-end communication over the network and provides service to upper-layer protocols (application layer). Simply, it is responsible for tracking the conversations (raw data) between multiple applications that are passing through the network.
NOTE
Transport Layer provides the logical communication between applications that runs on different hosts by simply adding a transport header on the raw data. The Protocol Data Unit (PDU) is now called a Segment.
Networking devices, like routers and switches, and end devices, like desktops and servers, have limitations on the amount of data that can be inserted in an IP packet. Because of that, the Transport Layer segments and reassemble the data (messages) between the sender and the receiver.
Whenever the hosts send a message into the network (internet), the Transport Layer prepares and separates the raw data (message) into smaller pieces of data for delivery. When received on the other hosts, the Transport Layer reassembles those smaller pieces of data and sends them to the upper layers.
The Application Layer has a lot of protocols that recognize the function of each data. Email traffic uses SMTP and POP3 protocols, while HTTP and HTTPS are the protocols used for web browsing. Each protocol is formatted differently based on its purpose.
If a different protocol is received on a specific application, then the application will drop the data. If the web server is receiving an SMTP protocol, then the data will be dropped as the web server is expecting to receive an HTTP or HTTPS protocol. The role of the Transport Layer is to ensure that the data is transmitted and delivered to the intended application.
Transport Layer Protocols – TCP and UDP
Every protocol uses a unique decimal number to ensure that the data is sent and received on the intended application as it passes through the network or Internet. The commonly used Transport Layer protocols responsible for message delivery are Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
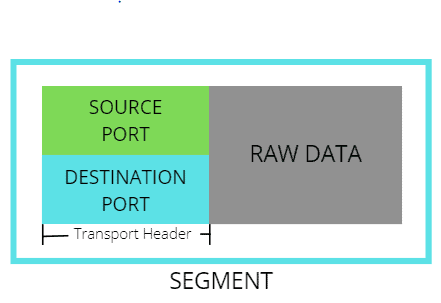
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol which means it guarantees the delivery of the message, while UDP is a connectionless protocol that sends the data without error correction. Under the TCP and UDP are port numbers that are used to distinguish the specific type of application. A specific port number is attached when sending the data so that the data will be received exactly to the intended application. The below diagram shows a segment in which the raw data is encapsulated by transport header (source and destination port).
Download our Free CCNA Study Guide PDF for complete notes on all the CCNA 200-301 exam topics in one book.
We recommend the Cisco CCNA Gold Bootcamp as your main CCNA training course. It’s the highest rated Cisco course online with an average rating of 4.8 from over 30,000 public reviews and is the gold standard in CCNA training:

CCNA 200-301 Tutorials
Introduction
- About Us
- What is CCNA?
- New CCNA exam - 200-301
- Free Cisco CCNA Study Guide
- Recommended CCNA Study Resources
Introduction to Networking
- What is a Network?
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- OSI & TCP/IP Models
- TCP/IP Suite of Protocols
- Encapsulation
Cisco Operating System IOS
- Cisco IOS Overview
- Ports on an IOS Device
- Auxiliary Port on a Cisco Router
- Cisco Console Rollover Cable
- Get Help in IOS
- IOS Command Modes
- Run Privileged Commands Within Global Config Mode
- Pipe Character in IOS
- Running & Startup Configuration
The Transport Layer
- Transport Layer Explanation – Layer 4 of the OSI Model
- Ports Explained
- TCP Explained
- TCP Three-Way Handshake
- UDP explained
The Network Layer
- IP Header
- Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast Addresses
- Types of IP Addresses
IPv4 Addressing
- What is Ipv4 Address and What is its Role in the Network?
- Converting the IP Address - Decimal to Binary
- Subnet Mask
- Classes of IP Addresses
Subnetting
- Subnetting Explained
- CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)
- Create Subnets
- Understanding Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM)
- Private IP Addresses Explained
The Data-Link Layer
- Ethernet Explained
- Ethernet Frame
- MAC & IP Addresses
The Physical Layer
- Types of Ethernet Cabling
- IEEE Ethernet Standards
- Types of Ethernet Cables – Straight-Through and Crossover
- Cisco PoE Explained - What is Power over Ethernet?
Cisco Network Devices
- Network Devices
- Network Hubs Explained
- Network Switch Explained
- CSMA/CD
- Collision & Broadcast Domain
- How Switches Work
- Layer 2 Switching
- Network Router Explained
- What Is Layer 3 Switch and How it Works in Our Network?
Life of a Packet
- What is Domain Name System (DNS) and How Does it Work?
- Map Hostnames to IP Addresses
- Configure Cisco Device as DNS client
- How to Configure a Cisco Router as a DNS Server?
- no ip domain-lookup Command
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Explained
- The ARP Table on a Cisco Router
Router & Switch Basic Configuration
- IOS Basic Commands
- Configure an IP Address on a Switch
- Configure Descriptions
- Interface Range Command
- Power on a Cisco Device
- Half Duplex and Full Duplex
- Configure Speed and Duplex
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) overview
- show Command
- show interfaces status Command
- Interface Status Codes
- show version Command
Cisco Device Management
- Types of Memory on a Cisco Device
- IOS Boot Sequence
- How to Reset a Cisco Router or Switch to Factory Default
- IOS files
- Backing up IOS Configuration
- FTP & TFTP
- Copy Files with FTP
- How to Upgrade Cisco IOS
- Cisco more Command
- Erasing Configuration Files
Basic Network Troubleshooting
- Network Troubleshooting Methodology and Techniques
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- Ping Explained
- Extended Ping Command
- Traceroute Explained
- traceroute Command
- show processes Command
IPv4 Routing
- What is IP Routing?
- Local Routes and How they Appear in the Routing Table
- Connected, Static, & Dynamic Routes
- Floating Static Route - Explanation and Configuration
- Default Static Route
- Create a Static Host Route
- What is a Static Summary Route? Explained and Configured
Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Routing Protocols
- Comparing Internal Routing Protocols (IGPs)
- Administrative Distance & Metric
- Equal Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) Explanation & Configuration
- Understanding Loopback Interfaces and Loopback Addresses
- passive-interface Command
Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP)
- RIP Overview
- Advertise Default Routes Using RIP
- Configuring RIPv2
- EIGRP Overview
- EIGRP Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL)
- EIGRP Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP)
- Wildcard Masks
- Wildcard Mask in EIGRP
- EIGRP Automatic & Manual Summarization
- EIGRP Summary
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- OSPF Overview
- Differences Between OSPF and EIGRP
- Cisco Bandwidth Command vs Clock Rate and Speed Commands
- OSPF Cost - OSPF Routing Protocol Metric Explained
- OSPF Configuration
- Designated & Backup Designated Router
- OSPF Passive Interface - Configuration and Why it is Used
- OSPF Default-Information Originate and the Default Route
- OSPF Load Balancing - Explanation and Configuration
- OSPF Summarization
- Troubleshooting OSPF and OSPF Configuration Verification
- OSPF Network Types - Point-to-Point and Broadcast
- OSPF Summary
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
- Cisco Three-Layer Hierarchical Model
- Collapsed Core and Three-Tier Network Architectures
- What is Spine and Leaf Network Architecture?
- What is a VLAN?
- Frame Tagging
- Configuring VLANs
- Access and Trunk Ports
- Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
- IEEE 802.1Q
- Configuring Access & Trunk Ports
- Configuring Voice VLANs
- Configuring Allowed VLANs
- Cisco Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) Explained
- What is VTP?
- VTP Modes
- VTP Configuration
Inter-VLAN Routing
- Configure interVLAN Routing
- Configure Cisco ROAS Router On A Stick
- Cisco Layer 3 Switch InterVLAN Routing Configuration
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- DHCP & DNS
- Configure Cisco Router as DHCP Server
- DHCP Relay Agent
- Configure Cisco Router as a DHCP Client
- APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing)
Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP)
- What is Network Redundancy and What are its Benefits?
- Cisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) Explained
- Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Explained
- Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Configuration
- Cisco Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) Preempt Command
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- What is STP?
- Network Bridge Explained
- How STP Works
- Electing the Root Switch in STP
- Spanning Tree Priority: Root Primary and Root Secondary
- Selecting STP Root Port
- Selecting STP Designated Port (DP)
- Spanning Tree Modes: MSTP, PVST+, and RPVST+
- What is RSTP?
- How RSTP Works
- Configuring RSTP
- Cisco HSRP and Spanning Tree Alignment Configuration
- Spanning Tree Portfast, BPDU Guard, Root Guard Configuration
EtherChannel
- What is EtherChannel and Why Do We Need It?
- EtherChannel Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
- EtherChannel Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Multichassis EtherChannel (MEC) and MEC Options
- Cisco Layer 3 EtherChannel - Explanation and Configuration
Switch Security
- What is DCHP Snooping? - Explanation and Configuration
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) Explanation & Configuration
- What is 802.1X Authentication and How it Works?
- Port Security
- Cisco Port Security Violation Modes Configuration
Access Control List (ACL)
- What are ACLs?
- Types of ACLs
- Configuring Standard ACLs
- Configuring Extended ACLs
- Configuring Named ACLs
Network Address Translation (NAT)
- What is NAT?
- Static NAT
- Dynamic NAT
- Port Address Translation (PAT) Configuration
IPv6 Addressing and Routing
- What is IPv6?
- IPv6 Address Format
- IPv6 Interface Identifier
- Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
- Types of IPv6 Addresses
- How to Configure IPv6
- IPv6 SLAAC - Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- IPv6 Routing - Static Routes Explained and Configured
- IPv6 Default Static Route and Summary Route
- IPv6 Routing Protocols
- Neighbor Discovery Protocol - NDP Overview
Wide Area Networks (WAN)
- Wide Area Network
- Cisco VPN - What is VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
- WAN Connection Types - Explanation and Examples
- Leased Line Definition, Explanation, and Example
- Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Explained & Configured
- What is PPPoE? Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet
- The Different Wide Area Network (WAN) Topologies
Security Concepts
- Cybersecurity Threats and Common Attacks Explained
- The Different Types of Firewalls Explained
- Firewalls, IDS, and IPS Explanation and Comparison
- Cisco Cryptography: Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
- HTTP and HTTPS explained
- Cyber Threats Attack Mitigation and Prevention
Network Device Security
- Telnet & SSH
- Setting Up Telnet
- Setting Up SSH
- Cisco Console Port Security
- exec-timeout Command
- Encrypt Local Usernames and Passwords
- Cisco Privilege Levels - Explanation and Configuration
- What is AAA? Authentication, Authorization, & Accounting
- Configuring AAA on Cisco Devices – RADIUS and TACACS+
- Configuring a Cisco Banner: MOTD, Login, & Exec Banners
- Configure Timezone and Daylight Saving Time (DST)
- NTP (Network Time Protocol)
- Configure NTP on a Cisco Router
Network Device Management
- Syslog Explained
- Syslog Message Format
- Cisco IOS Syslog Logging Locations
- logging synchronous Command
- debug Command
- terminal monitor Command
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- SNMPv3 Overview and Configuration
Quality of Service (QoS)
- Quality of Service (QoS) and its Effect on the Network
- Quality of Service (QoS) Classification and Marking
- Quality of Service (QoS) Queues and Queuing Explained
- Quality of Service (QoS) Traffic Shaping and Policing
- Quality of Service (QoS) Network Congestion Management
Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing - Definition, Characteristics, & Importance
- What is Server Virtualization, its Importance, and Benefits?
- Network Virtualization and Virtualizing Network Devices
- Cloud Computing Service Models - IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
- Cloud Deployment Models - Explanation and Comparison
- The Different WAN to Cloud Connectivity Options
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Wireless Networks
- What is Wireless Network and What are its Types?
- Wireless Access Point Operation Explained
- Autonomous AP Access Point Configuration
- Lightweight Access Point (AP) Configuration
- Cisco Wireless Architectures Overview and Examples
- Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Deployment Models
- 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz WiFi Frequency Spectrum
- Understanding WiFi Security - WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3
Network Automation and Programmability
- What is Network Automation and Why We Need It?
- Network Programmability - Git, GitHub, CI/CD, and Python
- Data Serialization Formats - JSON, YAML, and XML
- SOAP vs REST: Comparing the Web API Services
- Model-Driven Programmability: NETCONF and RESTCONF
- Configuration Management Tools - Ansible, Chef, & Puppet
- Cisco SDN - Software Defined Networking Explained
- Cisco DNA - Digital Network Architecture Overview
- Cisco IBN - Intent-Based Networking Explained
- Cisco SD-Access (Software-Defined Access) Overview
- Cisco SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN) Overview & Architecture
CCNP ENCOR 350-401 Tutorials



